20230721 题组题解报告
前言
做了此题,受教练逼迫特来写一篇题解
Warning
为表诚意,一下题目的代码皆为完整的正确的代码,您可以拿走对拍,但请不要抄袭,如果您抄袭了,我也没有办法。
T1 游戏 (game)
我妹有找到链接
题意简述
Alice 每次有 $\frac{1}{2^p}$ 的概率 $+2^{p-1}$($p$ 可任取),Bob 每次有 $\frac12$ 的概率 $+1$
Alice 先手,初值均为 $0$ ,先 $\ge n \space (1\le n \le 500)$ 者获胜,求 Alice 最优策略下获胜的概率
分析
概率 DP,反正我考场上没有想出来。
以 $f_{i,j}$ 表示 Alice 先手时,Alice 剩 $i$ 分,Bob 剩 $j$ 分,Alice 先手时获胜的概率。
状态转移方程
设上一轮 Alice $p$ 取值是 $k$
- Alice 成功 Bob 成功 $\frac{1}{2^k} \times \frac12 \times f_{i-2^{k-1},j-1}$
- Alice 成功 Bob 失败 $\frac{1}{2^k} \times \frac12 \times f_{i-2^{k-1}, j}$
- Alice 失败 Bob 成功 $(1-\frac1{2^k})\times \frac12 \times f_{i, j-1}$
- Alice 失败 Bob 失败 $(1-\frac1{2^k})\times \frac12 \times f_{i, j}$
所以,对于 Alice 取 $k$ 的情况
\[\begin{gather} f_{i, j}=\frac1{2^{k+1}}(f_{i-2^{k-1},j-1}+f_{i-2^{k-1},j}) +(1-\frac1{2^k})\frac12 f_{i, j-1} + (1-\frac1{2^k})\frac12f_{i, j} \\ \Leftrightarrow f_{i, j}=\frac{ \frac1{2^k} (f_{i-2^{k-1}, j-1}+f_{i-2^{k-1}, j})+(1-\frac1{2^k})f_{i, j-1} } { 1+\frac1{2^k} } \end{gather}\]对于所有情况
\[f_{i, j}=\min_{k \in N_+} \{ \frac{ \frac1{2^k} (f_{i-2^{k-1}, j-1}+f_{i-2^{k-1}, j})+(1-\frac1{2^k})f_{i, j-1} } { 1+\frac1{2^k} } \}\]边界条件
\[\begin{gather}f_{a, i} =1 \space (i \in [0, n], a \le 0)\\ f_{i, a} =0 \space (i \in [1, n], a \le 0) \end{gather}\]注意 $k$ 的范围好像要枚举到 $\log_2(4n)$
$O(n^2\log n)$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define FILE(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin);\
freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define REP(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<=(b); ++i)
#define REPd(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i>=(b); --i)
inline ll rd(){
ll r=0, k=1; char c; while(!isdigit(c=getchar())) if(c=='-') k=-k;
while(isdigit(c)) r=r*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); return r*k;
}
const int N=550;
long double f[N][N], ans; // long double 更精确
int n;
int main(){
FILE(game);
n=rd(), f[0][0]=1;
REP(i, 1, n) f[0][i]=1, f[i][0]=0;
REP(i, 1, n) REP(j, 1, n){
REP(k, 1, 15){
int tmp=i-(1<<(k-1));
if(tmp<0) tmp=0; // 注意判负
long double t1=f[tmp][j],
t2=f[tmp][j-1],
t3=f[i][j-1];
f[i][j]=max(f[i][j], ((1.0/(1<<k))*(t1+t2)+(1-(1.0)/(1<<k))*t3)/(1+1.0/(1<<k)));
}
}
printf("%.6f", (double)f[n][n]);
return 0;
}
T2 秘密文件 (cipher)
P2400 秘密文件 - 洛谷 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
题意简述
将字符串进行压缩到最短,如 AAAAAAAAAABABABCCD => 9(A)3(AB)CCD
分析
有点 DP 的感觉
$f_{i, j}$ 表示 $S[i, j]$ 这段压缩到最短的长度,$Ans_{i,j}$ 表示 $S[i, j]$ 这段压缩到最短的结果
\[f_{i, j}= \min_{i \le k \lt j} \{ f_{i, k} +f_{k+1, j}\}\]或者自己段重复部分压缩
还是看代码吧
$O(玄学\times n^3)$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define FILE(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin);\
freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define REP(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<=(b); ++i)
#define REPd(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i>=(b); --i)
inline ll rd(){
ll r=0, k=1; char c; while(!isdigit(c=getchar())) if(c=='-') k=-k;
while(isdigit(c)) r=r*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); return r*k;
}
char ch[110];
int f[110][110], len;
string ans[110][110];
int dfs(int l=1, int r=len){
if(l==r) return ans[l][r]=ch[l], f[l][r]=1;
if(f[l][r]!=0) return f[l][r];
REP(k, l, r-1){ // 由 [l,k] [k+1,j] 更新
dfs(l, k); dfs(k+1, r);
if(f[l][r]==0||f[l][k]+f[k+1][r]<f[l][r]){
f[l][r]=f[l][k]+f[k+1][r];
ans[l][r]=ans[l][k]+ans[k+1][r];
}
}
REP(i, 1, (r-l+1)/2){ // 自己有重复段, i为段长, b为段数
if((r-l+1)%i) continue;
int b=(r-l+1)/i;
stringstream tmp;
string tmp2;
tmp<<b<<'(';
REP(k, l, l+i-1){ // 暴力比较
REP(j, 1, b-1){
if(ch[k+j*i]!=ch[k+(j-1)*i]){
goto out;
}
}
}
dfs(l, l+i-1);
tmp<<ans[l][l+i-1]<<')';
tmp>>tmp2;
if(f[l][r]==0||f[l][r]>tmp2.length()){
f[l][r]=tmp2.length();
ans[l][r]=tmp2;
}
out:;
}
return f[l][r];
}
int main(){
FILE(cipher);
scanf("%s", ch+1);
ch[0]='!';
len=strlen(ch)-1;
dfs();
puts(ans[1][len].c_str());
return 0;
}
T3 牛的杂技 (Cow Acrobats)
题意简述
序列 ${ a_i }$ 的每一项 $a_i$ 有两个属性 $a_i.w$ 和 $a_i.s$
求 ${a_i}$ 的一个排列使
\[\max_{1\le i\le n} \{ \sum_{j=1}^{i-1} a_j.w -a_i.s\}\]最小,输出最小值即可
分析
贪心
这道题我是机缘巧合做出来的
考场上我是先假设最大值会在 $i=n$ 时取到推出要最大化 $a_n.w+a_n.s$
然后又发现如果最大值在 $i=k\space (k<n)$ 取到时可以推出 $\forall j>i, a_i.w+a_i.s<a_j.w+a_j.s$
然后,我就没有理由的大胆假设最优情况是按照 $w+s$ 升序排序
嗯,就 A 了
严谨证明
假设相邻两项分别为 $a_i$ 和 $a_{i+1}$
若 $a_i$ 在 $a_{i+1}$ 前更优
则考虑交换两项前后
\[\begin{gather} \max(\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} a_j.w-a_i.s, \sum_{j=1}^{i} a_j.w-a_{i+1}.s) \\< \max(\sum_{j=1}^{i-1} a_j.w-a_{i+1}.s, \sum_{j=1}^{i-1} a_j.w+a_{i+1}.w-a_{i}.s) \\ \Leftrightarrow \max(-a_i.s, a_i.w-a_{i+1}.s) < \max(-a_{i+1}.s, a_{i+1}.w-a_i.s) \\ \Leftrightarrow \max(a_{i+1}.s, a_i.w+a_i.s) <\max(a_i.s, a_{i+1}.w+a_{i+1}.s)\space _{(1)} \\ a_i.s < a_i.w+a_i.s \le \max(a_{i+1}.s, a_i.w+a_i.s)\space _{(2)} \\ (1)(2)\Rightarrow a_i.s<a_i.w+a_i.s<\max(a_i.s, a_{i+1}.w+a_{i+1}.s) \\ \Rightarrow a_i.w+a_i.s<a_{i+1}.w+a_{i+1}.s \end{gather}\]$O(n\log n)$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define FILE(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin);\
freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define REP(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<=(b); ++i)
#define REPd(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i>=(b); --i)
inline ll rd(){
ll r=0, k=1; char c; while(!isdigit(c=getchar())) if(c=='-') k=-k;
while(isdigit(c)) r=r*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); return r*k;
}
const int N=50050;
ll n, sum, ans;
struct cow{
ll w, s;
bool operator<(const cow &y) const { // 代码多简单,我不用详述了吧
return w+s<y.w+y.s;
}
}c[N];
int main(){
FILE(acrobat);
n=rd();
REP(i, 1, n){
c[i].w=rd(), c[i].s=rd();
}
sort(c+1, c+n+1);
ans=-c[1].s;
REP(i, 1, n){
ans=max(ans, sum-c[i].s);
sum+=c[i].w;
}
printf("%lld", ans);
return 0;
}
T4 过路费 (cost)
CodeVS 1519 我妹有打开就不贴链接了
题意简述
给定一个无向图,和 $q$ 个询问包含 $S, T$ 最小化 $S$ 到 $T$ 路径上的最大边权,每个询问输出这个值
分析
最小生成树+LCA
这题还算明显…吧
首先是答案路径一定在最小生成树上
简证
考虑两点间有多条路径
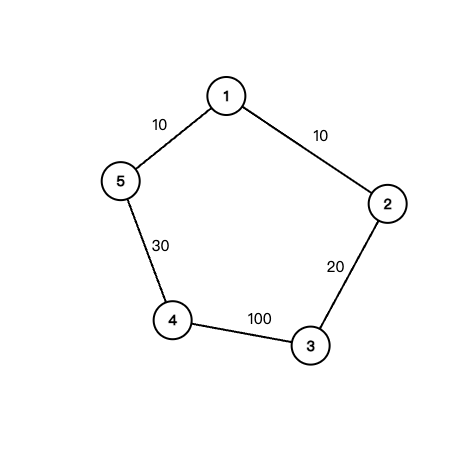
如图中 4, 2 两点有 <4, 5, 1, 2> 和 <4, 3, 2> 两条路径
而考虑最小生成树的过程
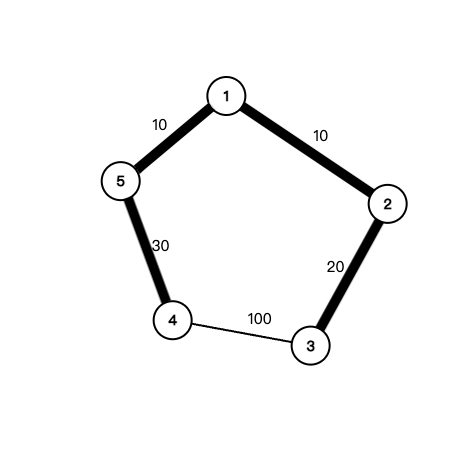
删去的边的端点一定由比它小的边连通
所以走树边的路径的最大边权一定小于其他路径的最大边权
(因为小于其中被删的边的边权)
证必
至于树上路径最大边权可以类似 LCA 的倍增方法,在维护一个 $mx[i][j]$
表示从 $i$ 点向上 $2^j$ 所经过的路径的边权最大值
更新方法
mx[i][0]=(i, fa[i]).v
mx[i][j]=max(mx[i][j-1], mx[pa[i][j-1]][j-1]);
$O(m\log m+q\log n)$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define FILE(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin);\
freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define REP(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<=(b); ++i)
#define REPd(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i>=(b); --i)
inline ll rd(){
ll r=0, k=1; char c; while(!isdigit(c=getchar())) if(c=='-') k=-k;
while(isdigit(c)) r=r*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); return r*k;
}
const int N=10010, M=100010;
ll n, m, q, mx[N][30];
int fat[N], dep[N], pa[N][30];
typedef pair<int, ll> pil;
vector<pil> g[N];
struct edge{
int a, b; ll w;
bool operator<(const edge &x) const {
return w<x.w;
}
}e[M];
int find(int x){
return x==fat[x]?x:fat[x]=find(fat[x]);
}
void kruskal(){
sort(e+1, e+m+1);
REP(i, 1, m){
int a=e[i].a, b=e[i].b, w=e[i].w;
if(find(a)!=find(b)){
g[a].push_back(make_pair(b, w));
g[b].push_back(make_pair(a, w));
fat[find(a)]=find(b);
}
}
}
void dfs(int x=1, int fa=0){
dep[x]=dep[fa]+1; pa[x][0]=fa;
REP(i, 1, 16) pa[x][i]=pa[pa[x][i-1]][i-1], mx[x][i]=max(mx[x][i-1], mx[pa[x][i-1]][i-1]);
for(vector<pil>::iterator i=g[x].begin(); i!=g[x].end(); ++i)
if(i->first!=fa){
mx[i->first][0]=i->second;
dfs(i->first, x);
}
}
ll lca_max(int x, int y){
if(dep[y]>dep[x]) swap(x, y);
int tmp=dep[x]-dep[y]; ll res=0;
REP(i, 0, 16) if(tmp&(1<<i)) res=max(res, mx[x][i]), x=pa[x][i];
REPd(i, 16, 0){
int xx=pa[x][i], yy=pa[y][i];
if(xx!=yy){
res=max(res, mx[x][i]), res=max(res, mx[y][i]);
x=xx, y=yy;
}
}
return x==y?res:max(res, max(mx[x][0], mx[y][0]));
}
int main(){
FILE(cost);
n=rd(), m=rd();
REP(i, 1, n) fat[i]=i;
REP(i, 1, m) e[i].a=rd(), e[i].b=rd(), e[i].w=rd();
kruskal();
dfs();
q=rd();
while(q--){
int s=rd(), t=rd();
printf("%lld\n", lca_max(s, t));
}
return 0;
}
T5 加工零件 (work)
P5663 [CSP-J2019] 加工零件 - 洛谷 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
题意简述
太长了,简述不了,自己看上面的链接
分析
分层图最短路
对于 $a$ 到 $1$ 号节点,如果有一条路径是偶数
如图,$5$ 到 $1$,上面那条路径长度是偶数
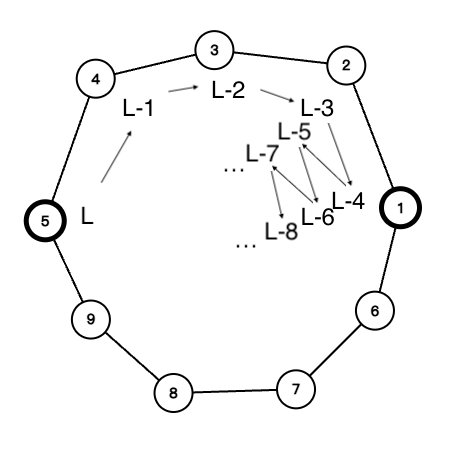
所以只要 $L-4, L-6, L-8, …$ 中有一个为 $0$ 即需要提供原材料
等价于
\[L\in \{x:x=2k,x\ge E,k\in Z\}\]其中 $E$ 表示这条路径边数
若路径长为奇数
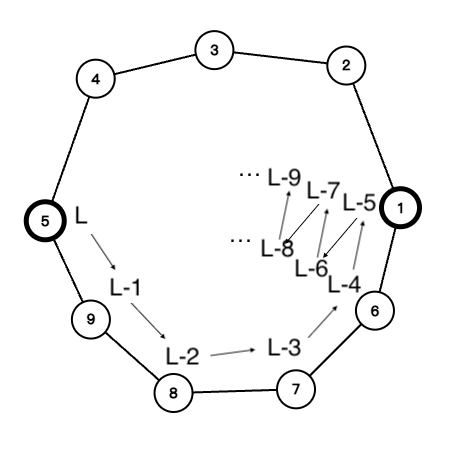
等价于
\[L\in \{x:x=2k+1,x\ge E,k\in Z\}\]其中 $E$ 表示这条路径边数
要尽可能满足 $x \ge E$ 的条件,取最短路即可
所以只需找出 $1$ 到 $a$ 的奇数最短路和偶数最短路
考虑分层图
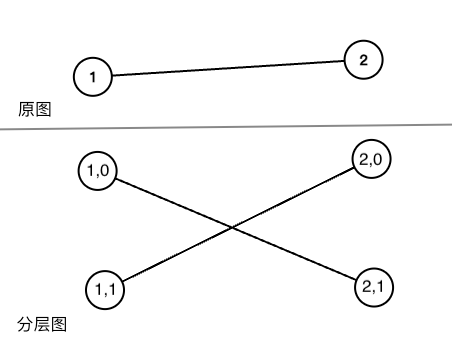
将原来的点 $i$ 拆成 $i,0$ 和 $i,1$ 分别代表到 $i$ 时路径为偶数和奇数
将原来的边 $i-j$ 改成 $i,0-j,1$ 和 $i, 1-j,0$
然后以 $1, 0$ 为原点跑单源最短路,这里边权唯一所以跑 BFS 即可
当然你跑 Dijkstra 或 SPFA 也行
这里其实可以建图时按原图建,跑 BFS 时当作分层图跑
BFS:$O(n+m+q)$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define FILE(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin);\
freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define REP(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<=(b); ++i)
#define REPd(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i>=(b); --i)
inline ll rd(){
ll r=0, k=1; char c; while(!isdigit(c=getchar())) if(c=='-') k=-k;
while(isdigit(c)) r=r*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); return r*k;
}
const int N=1e5+10;
ll n, m, q, d[N][2], l;
int a, b, v[N][2];
char ans[2][10]={"No", "Yes"};
vector<int> g[N];
#define pb push_back
struct node{
int u, f;
node(int u, int f):u(u), f(f){}
};
void bfs(){
memset(d, 0x7f, sizeof(d));
memset(v, 0, sizeof(v));
queue<node> p;
d[1][0]=0; v[1][0]=1;
p.push(node(1, 0));
while(!p.empty()){
node u=p.front(); p.pop();
for(vector<int>::iterator i=g[u.u].begin(); i!=g[u.u].end(); ++i){
node y=node(*i, 1-u.f); // 按照分层图转移
if(v[y.u][y.f]) continue;
d[y.u][y.f]=d[u.u][u.f]+1;
v[y.u][y.f]=1;
p.push(y);
}
}
}
int main(){
FILE(work);
n=rd(), m=rd(), q=rd();
while(m--) a=rd(), b=rd(), g[a].pb(b), g[b].pb(a); // 建原图
bfs();
while(q--){
a=rd(), l=rd();
// 条件判断
printf("%s\n", ans[((l&1)&&l>=d[a][1])||((l%2==0)&&l>=d[a][0])]);
}
return 0;
}
T6 奶牛政坛 (Cow Politics)
P2971 [USACO10HOL] Cow Politics G - 洛谷 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
题意简述
给定一颗树,每个节点都属于某一个集团,而且每个集团至少包括两个节点。求每个集团离得最远的两个节点(沿着双向道路行走)的距离。
分析
直径+LCA
这题考场时觉得毫无头绪
看了题解发现这么简单
根据直径的性质,可以类似知道以一个根结点到每个集团内深度最深的点一定是每个集团内的“直径”中的端点
将其作为其集团的代表
求集团内每个点到他的距离取最大值即可
求距离可用 LCA 求
$O(n\log n)$
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
#define FILE(x) freopen(#x".in", "r", stdin);\
freopen(#x".out", "w", stdout)
#define REP(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i<=(b); ++i)
#define REPd(i, a, b) for(int i=(a); i>=(b); --i)
inline ll rd(){
ll r=0, k=1; char c; while(!isdigit(c=getchar())) if(c=='-') k=-k;
while(isdigit(c)) r=r*10+c-'0', c=getchar(); return r*k;
}
const int N=200010;
ll n, k, a[N], ans[N], f[N], p, rt, pa[N][30], dep[N];
vector<int> g[N];
void dfs(int x=rt, int fa=0){ // 普通的 DFS
dep[x]=dep[fa]+1; pa[x][0]=fa;
REP(i, 1, 20) pa[x][i]=pa[pa[x][i-1]][i-1];
for(vector<int>::iterator i=g[x].begin(); i!=g[x].end(); ++i){
dfs(*i, x);
}
}
int lca(int x, int y){ // 普通的 LCA
if(dep[x]<dep[y]) swap(x, y);
int t=dep[x]-dep[y];
REP(i, 0, 20) if(t&(1<<i)) x=pa[x][i];
REPd(i, 20, 0){
int xx=pa[x][i], yy=pa[y][i];
if(xx!=yy) x=xx, y=yy;
}
return x==y?x:pa[x][0];
}
int main(){
FILE(cowpol);
n=rd(), k=rd();
REP(i, 1, n) a[i]=rd(), p=rd(), g[p].push_back(i), rt=p==0?i:rt;
dfs();
REP(i, 1, n) if(dep[f[a[i]]]<dep[i]) f[a[i]]=i; // 每个集团的最远点
// 集团距离更新
REP(i, 1, n) ans[a[i]]=max(ans[a[i]], dep[i]+dep[f[a[i]]]-2*dep[lca(i, f[a[i]])]);
REP(i, 1, k) printf("%lld\n", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
